C++
C++
目录
C++标准库
C++标准库——体系结构与内核分析(C++ Standard Library —— architecure & sources)
- 体系结构,指C++标准库主要分为6个部件
- 内核分析,指会分析 source code 源代码
参考:
- 【B站】C++标准库(STL)与泛型编程,侯捷老师的课
【CSDN】别人的听课笔记- P3~P7不太懂,测试好难
- C++ 基准测试 - std
list - 书录
- 《The C++ Standard Library》
- 《STL源码剖析》侯捷(自己推荐自己的书2333)
简概
简概
标准库特点
- 主要使用模板做的(Generic Programming(GP、泛型编程))
- C++标准库(C++ Standard Library)包含 标准模板库(Standard Template Library)
- 头文件问题
- C++标准库的头文件不带扩展名(.h)
- 新式 C头文件不带扩展名,例
#include <cstdio> - 旧式 C头文件带扩展名,仍可使用,例
#include <stdio.h> - 新式 C头文件组件封装于std命名空间中,使用
using namespace std;orusing std::cout; - 旧式 C头文件组件不封装与std头文件中
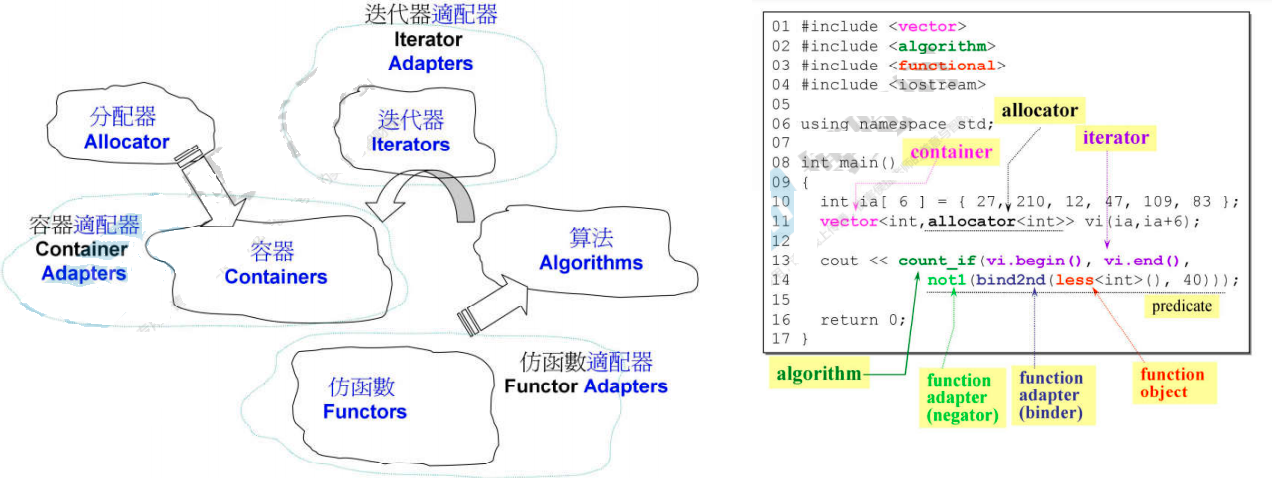
STL六大组件
STL六大组件,包括
- 容器 (container)
- 分配器 (allocator)
- 容器需要一个分配器,若不写则容器内部会有一个默认分配器
- 例
vector<int,allocator<int>> vi(ia,ia+6);可简写为vector<int> vi(ia);
- 算法 (algorithm)
- 迭代器 (iterator)
- 适配器 (adapter)
- 仿函数 (functor)
结构
时间复杂度
- 或:常数时间(constant time)
- :线性时间(linear time)
- :次线性时间(sub-linear time)
- :平方时间(quadratic time)
- :立方时间(cubic time)
- :指数时间(exponential time)
- :介于线性及二次方成长的中间
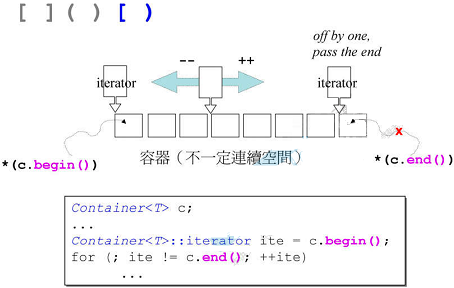
前闭后开区间
STL中的区间遵循前闭后开的表示方式,迭代器begin指向的是第一个元素的起点,end指向的是最后一个元素的下一个元素.
程序测试 - 容器
测试程序
/* 使用命名空间 */
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::string;
/* 输入并获取一个目标长整数 */
long get_a_target_long()
{
long target=0;
cout << "target (0~" << RAND_MAX << "): "; // 随机数?
cin >> target;
return target;
}
/* 输入并获取一个目标字符串 */
string get_a_target_string()
{
long target=0;
char buf[10];
cout << "target (0~" << RAND_MAX << "): "; // 随机数?
cin >> target;
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", target); // 将数值转换为字符串
return string(buf);
}
/* 比较 - 长整数方式 */
int compareLongs(const void* a, const void* b) // void 指针可以指向任意类型的数据
{
return (*(long*)a - *(long*)b); // 先转换指针类型再取指针值
}
/* 比较 - 字符串方式 */
int compareStrings(const void* a, const void* b)// void 指针可以指向任意类型的数据
{
if(*(string*)a > *(string*)b) // 先转换指针类型再取指针值
return 1;
else if(*(string*)a < *(string*)b)
return -1;
else
return 0;
}测试 - array
扩充:不可扩充
#include <array>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdlib> // qsort, bsearch, NULL
namespace test01
{
const long ASIZE = 500000L; // 数组大小
void test_array() {
cout << "\ntest_array().......... \n";
/** 创建操作 */
array<long, ASIZE> c; // 定义容器
/** 插入操作 */
clock_t timeStart = clock(); // 取时间戳
for (long i = 0; i < ASIZE; ++i) { // 随机填充满容器
c[i] = rand();
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl; // 所用的时间计时(时间戳相减)
cout << "array.size()= " << c.size() << endl; // 大小
cout << "array.front()= " << c.front() << endl; // 第一个元素(随机数)
cout << "array.back()= " << c.back() << endl; // 最后个元素(随机数)
cout << "array.data()= " << c.data() << endl; // 起点的地址
/** 排序 + 查找操作 */
long target = get_a_target_long(); // 获取一个长整数
timeStart = clock(); // 取时间戳
qsort(c.data(), ASIZE, sizeof(long), compareLongs); // 排序 - 长整数比较
long *pItem = (long*)bsearch(&target, (c.data()), ASIZE, sizeof(long), compareLongs); // 排序后二分查找 - 长整数比较
cout << "qsort()+bsearch(), milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl; // 所用的时间(时间戳相减)
if (pItem != NULL)
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
}输出
select: 1
test_array()..........
milli-seconds : 47
array.size()= 500000
array.front()= 3557
array.back()= 23084
array.data()= 0x47a20
target (0~32767): 20000
qsort()+bsearch(), milli-seconds : 187
found, 20000测试 - vector
扩充:底层是一段连续的内存空间,当容器满时进行扩容,将容器大小扩容为原来的两倍
namespace test02
{
void test_vector(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_vector().......... \n";
/** 创建操作 */
vector<string> c; // 定义容器
char buf[10];
/** 插入操作 */
clock_t timeStart = clock(); // 取时间戳
for (long i = 0; i < ASIZE; ++i) { // 随机填充满容器
try{
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand()); // 按format格式化为字符串
c.push_back(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p){ // 防止内存不足
cout << "i:" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl; // 所用的时间计时(时间戳相减)
cout << "array.size()= " << c.size() << endl; // 大小
cout << "array.front()= " << c.front() << endl; // 第一个元素(随机数)
cout << "array.back()= " << c.back() << endl; // 最后个元素(随机数)
cout << "array.data()= " << c.data() << endl; // 起点的地址
/** 排序 + 查找操作 */
// 直接find方法(在此例中更快)
string target = get_a_target_string();
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target);
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl << endl;
}
// 先排序后find方法
{
timeStart = clock();
sort(c.begin(), c.end()); // 这里是标准库里的sort
cout << "sort(), milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
timeStart = clock();
string *pItem = (string *)::bsearch(&target, (c.data()), c.size(), sizeof(string), compareStrings);
cout << "bsearch(), milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != NULL)
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl << endl;
}
}
}输出
select:2
how many elements:1000000
test_vector()..........
milli-seconds : 3063
vector.size()= 1000000
vector.front()= 4047
vector.back()= 2877
vector.data()= 0x2880020
vector.capacity()= 1048576 // 表示使用了1000000个元素后,还剩余48576个元素空间(浪费)
target (0~32767):23456
std::find(), milli-seconds : 0
found, 23456
sort(), milli-seconds : 2695
bsearch(), milli-seconds : 1
found, 23456测试 - list
扩充:多一个元素,非常节省内存
#include <list>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> // abort()
#include <cstdio> // snprintf()
#include <algorithm> // find()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
void test_list(long &value) {
cout << "\ntest_list().......... \n";
/** 创建操作 */
list <string> c;
char buf[10];
/** 插入操作 */
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for (long i = 0; i < value; ++i) {
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push_back(string(buf));
}
catch (exception &p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
cout << "list.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "list.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; // 357913941
cout << "list.front()= " << c.front() << endl;
cout << "list.back()= " << c.back() << endl;
/** 排序 + 查找操作 */
// find方式
string target = get_a_target_string();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target);
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
timeStart = clock();
// 排序
c.sort(); // 这里是容器里实现的sort,不是标准库里的sort。一般前者效率更高
cout << "c.sort(), milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
}输出
how many elements:1000000
test_list()..........
milli-seconds : 3265
list.size()= 1000000
list.max_size()= 384307168202282325 ???
list.front()= 31411
list.back()= 7939
target (0~32767):23456
std::find(), milli-seconds : 4
found, 23456
c.sort(), milli-seconds : 3610测试 - forward_list
扩充:多一个元素,非常节省内存
#include <forward_list>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> // abort()
#include <cstdio> // snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
void test_forward_list(long &value) {
cout << "\ntest_forward_list().......... \n";
forward_list <string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for (long i = 0; i < value; ++i) {
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push_front(string(buf)); // 头部插入,因为后部操作要遍历整个链表
}
catch (exception &p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
cout << "forward_list.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //536870911
cout << "forward_list.front()= " << c.front() << endl;
string target = get_a_target_string();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target);
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
timeStart = clock();
c.sort();
cout << "c.sort(), milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
}输出
how many elements:1000000
test_forward_list()..........
milli-seconds : 296
forward_list.max_size()= 461168601842738790
forward_list.front()= 11513
target (0~32767):23456
std::find(), milli-seconds : 9
found, 23456
c.sort(), milli-seconds : 3706测试 - slist
测试略
和forward_list基本一样。但不属于C++ STL,是旧版本就有的,使用要#include <ext\slist>
测试 - deque
**扩充:每次扩充一个buffer。**deque是分段连续,抽象是连续的,但具体实现上是分为很多段的,每段叫一个buffer(也就是说添加多个元素后,占用内存才会多上一点)
#include <deque>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> // abort()
#include <cstdio> // snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
void test_deque(long &value) {
cout << "\ntest_deque().......... \n";
deque <string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for (long i = 0; i < value; ++i) {
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push_back(string(buf));
}
catch (exception &p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
cout << "deque.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "deque.front()= " << c.front() << endl;
cout << "deque.back()= " << c.back() << endl;
cout << "deque.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl;
string target = get_a_target_string();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target);
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
timeStart = clock();
sort(c.begin(), c.end());
cout << "sort(), milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
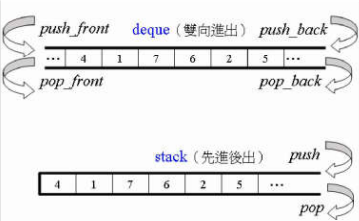
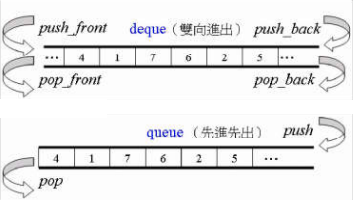
}测试 - stack 和 queue
stack和queue底层是通过deque实现的,从设计模式上来说,这两种容器本质上是deque的适配器
但不同于deque:这两个容器的元素进出是有严格顺序的,因此stack和queue不支持有关迭代器的操作
stack | queue |
|---|---|
 |  |
demo
#include <stack>
#include <queue>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> // abort()
#include <cstdio> // snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
void test_stack(long &value) {
cout << "\ntest_stack().......... \n";
stack <string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for (long i = 0; i < value; ++i) {
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push(string(buf));
}
catch (exception &p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
cout << "stack.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "stack.top()= " << c.top() << endl;
c.pop();
cout << "stack.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "stack.top()= " << c.top() << endl;
}
void test_queue(long &value) {
cout << "\ntest_queue().......... \n";
queue <string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for (long i = 0; i < value; ++i) {
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push(string(buf));
}
catch (exception &p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
cout << "queue.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "queue.front()= " << c.front() << endl;
cout << "queue.back()= " << c.back() << endl;
c.pop();
cout << "queue.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "queue.front()= " << c.front() << endl;
cout << "queue.back()= " << c.back() << endl;
}输出
how many elements:300000
test_stack()..........
milli-seconds : 57
stack.size()= 300000
stack.top()= 17153
stack.size()= 299999
stack.top()= 31703
how many elements:300000
test_queue()..........
milli-seconds : 54
queue.size()= 300000
queue.front()= 6608
queue.back()= 29870
queue.size()= 299999
queue.front()= 7837
queue.back()= 29870测试 - multiset 和 multimap
multiset 和 multimap,即使重复也可以添加进去
multiset和multimap底层是使用红黑树实现的
因为multimap支持重复的key,因此不能使用重载的[]运算符进行插入
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> // abort()
#include <cstdio> // snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
void test_multiset(long &value) {
cout << "\ntest_multiset().......... \n";
/** 填充 */
multiset <string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for (long i = 0; i < value; ++i) {
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.insert(string(buf)); // insert
}
catch (exception &p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
cout << "multiset.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "multiset.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl;
/** 查找 */
string target = get_a_target_string();
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); //比 multiset::find(...) 慢很多
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target); //比 std::find(...) 快很多
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
}
void test_multimap(long &value) {
cout << "\ntest_multimap().......... \n";
multimap<long, string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for (long i = 0; i < value; ++i) {
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
// multimap 不可使用 [] 做 insertion,map则可以
c.insert(pair<long, string>(i, buf));
}
catch (exception &p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
cout << "multimap.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "multimap.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //178956970
long target = get_a_target_long();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target);
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, value=" << (*pItem).second << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
c.clear();
}输出
// multiset
how many elements:1000000
test_multiset()..........
milli-seconds : 5202
multiset.size()= 1000000
multiset.max_size()= 288230376151711743
target (0~32767):23456
std::find(), milli-seconds : 75
found, 23456
c.find(), milli-seconds : 0
found, 23456
// multimap
how many elements:1000000
test_multimap()..........
milli-seconds : 1423
multimap.size()= 1000000
multimap.max_size()= 256204778801521550
target (0~32767):23456
c.find(), milli-seconds : 0
found, value=13328测试 - set 和 map
set 和 map 的原因是,这两个不能重复,重复的话会添加不进去
代码:略
set 输出
select: 13
how many elements: 1000000
test_set()..........
milli-seconds: 3922
set.size()= 32768 // 因为会重复,size比elements少
set.max_size()= 214748364
target (0~32767): 23456
::find(),milli-seconds: 0
found, 23456
c.find(),milli-seconds: 0
found, 23456map 输出
select: 14
how many elements: 1000000
test_set()..........
milli-seconds: 4890
set.size()= 1000000 // 一样,因为key不重复
set.max_size()= 178956970
target (0~32767): 23456
c.find(),milli-seconds: 0
found, 23456测试 - unordered_multiset 和 unordered_multimap
扩充:unordered_multiset和unordered_multimap元素数目达到篮子个数时,则容器扩容,将篮子数组扩充约一倍
#include <unordered_set>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> // abort()
#include <cstdio> // snprintf()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
void test_unordered_multiset(long &value) {
cout << "\ntest_unordered_multiset().......... \n";
unordered_multiset <string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for (long i = 0; i < value; ++i) {
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.insert(string(buf));
}
catch (exception &p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //357913941
cout << "unordered_multiset.bucket_count()= " << c.bucket_count() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.load_factor()= " << c.load_factor() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.max_load_factor()= " << c.max_load_factor() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multiset.max_bucket_count()= " << c.max_bucket_count() << endl;
for (unsigned i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
cout << "bucket #" << i << " has " << c.bucket_size(i) << " elements.\n";
}
string target = get_a_target_string();
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); //比 unordered_multiset::find() 慢很多
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target); //比 std::find() 快很多
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
}
void test_unordered_multimap(long &value) {
cout << "\ntest_unordered_multimap().......... \n";
unordered_multimap<long, string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for (long i = 0; i < value; ++i) {
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
//multimap 不可使用 [] 進行 insertion
c.insert(pair<long, string>(i, buf));
}
catch (exception &p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
cout << "unordered_multimap.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "unordered_multimap.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl;
long target = get_a_target_long();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target);
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, value=" << (*pItem).second << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}输出
how many elements:1000000
test_unordered_multiset()..........
milli-seconds : 1476
unordered_multiset.size()= 1000000
unordered_multiset.max_size()= 384307168202282325
unordered_multiset.bucket_count()= 1832561 // 篮子的数量
unordered_multiset.load_factor()= 0.545684 // 装载因子
unordered_multiset.max_load_factor()= 1
unordered_multiset.max_bucket_count()= 384307168202282325
bucket #0 has 0 elements.
bucket #1 has 0 elements.
bucket #2 has 0 elements.
bucket #3 has 0 elements.
bucket #4 has 0 elements.
bucket #5 has 0 elements.
bucket #6 has 0 elements.
bucket #7 has 34 elements.
bucket #8 has 0 elements.
bucket #9 has 0 elements.
target (0~32767):23456
std::find(), milli-seconds : 104
found, 23456
c.find(), milli-seconds : 1
found, 23456
how many elements:1000000
test_unordered_multimap()..........
milli-seconds : 1051
unordered_multimap.size()= 1000000
unordered_multimap.max_size()= 384307168202282325
target (0~32767):23456
c.find(), milli-seconds : 0
found, value=20464测试 - unordered_set 和 unordered_map
略
程序测试 - 分配器 allocator
简概
分配器 (allocator)
- 容器需要一个分配器,若不写则容器内部会有一个默认分配器
- 例
vector<int,allocator<int>> vi(ia,ia+6);可简写为vector<int> vi(ia);
容器对分配器的使用(默认都是使用std::allocator分配器)
template<typename _Tp, typename _Alloc=std::allocator<_Tp>>
class vector:protected _Vector_base<_Tp, _Alloc>
template<typename _Tp, typename _Alloc=std::allocator<_Tp>>
class list:protected _List_base<_Tp, _Alloc>
template<typename _Tp, typename _Alloc=std::allocator<_Tp>>
class depue:protected _Deque_base<_Tp, _Alloc>
template<typename _Key, typename _Compare=std::less<_Key>,
typename _Alloc=std::allocator<_Tp>>
class set
template<typename _Key, typename _Compare=std::less<_Key>,
typename _Alloc=std::allocator<_Tp>>
class map
template<class _Value,
class _Hash=hash<_Value>,
class _Pred=std::equal_to<_Value>,
class _Alloc=std::allocator<_Value>>
class unordered_set
template<class _Key, class _Tp,
class _Hash=hash<_Value>,
class _Pred=std::equal_to<_Value>,
class _Alloc=std::allocator<_Value>>
class unordered_mapSTL容器默认的分配器是std::allocator,除此之外 gcc 额外定义了几个分配器,其头文件均在目录ext下
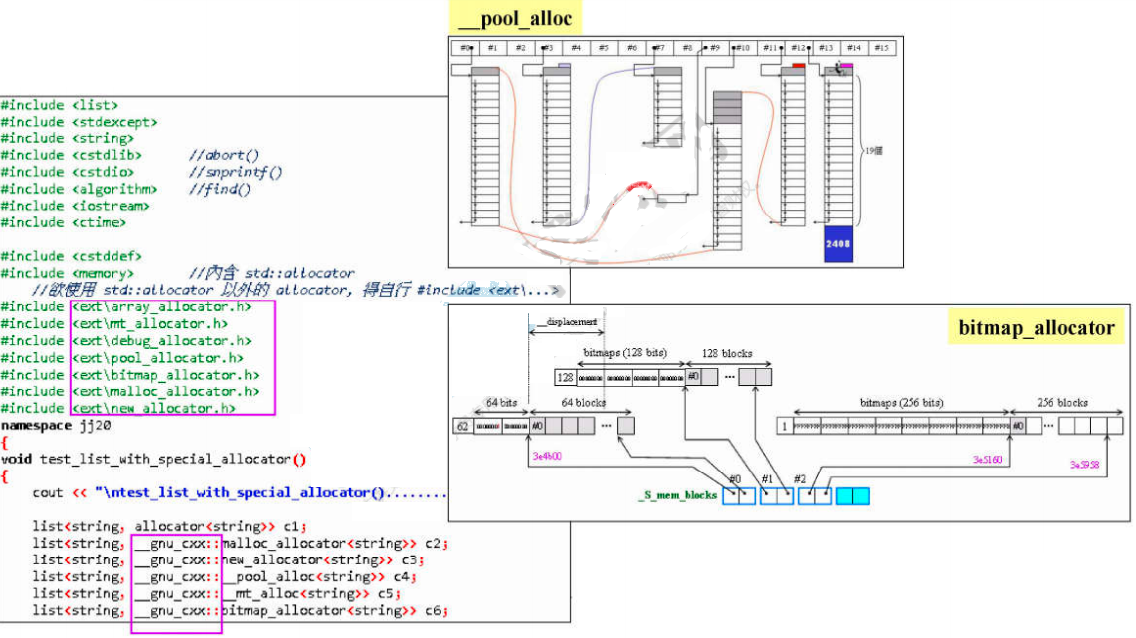
(该图演示了其中两种的分配器)
gcc额外定义的分配器均位于__gnu_cxx命名空间下.分配器一般用于构建容器,不会直接使用.因为分配器想要直接使用也不好用(使用free关键字时不需要指定回收内存的大小,而分配器的deallocate函数需要指定回收内存大小).
测试程序
#include <list>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib> // abort()
#include <cstdio> // snprintf()
#include <algorithm> // find()
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstddef>
#include <memory> //內含 std::allocator
//欲使用 std::allocator 以外的 allocator,得自行 #include <ext\...>
#ifdef __GNUC__
/* 这里是分配器的头文件(7种) */
#include <ext\array_allocator.h>
#include <ext\mt_allocator.h>
#include <ext\debug_allocator.h> // 调试
#include <ext\pool_allocator.h> // 内存池
#include <ext\bitmap_allocator.h>
#include <ext\malloc_allocator.h>
#include <ext\new_allocator.h>
#endif
//pass A object to function template impl(),
//而 A 本身是個 class template, 帶有 type parameter T,
//那麼有無可能在 impl() 中抓出 T, 創建一個 list<T, A<T>> object?
//以下先暫時迴避上述疑問.
void test_list_with_special_allocator() {
#ifdef __GNUC__
cout << "\ntest_list_with_special_allocator().......... \n";
/** list使用不同的分配器(6种) */
// 不能在 switch case 中宣告,只好下面這樣. // 1000000次
list <string, allocator<string>> c1; // 3140,这个是默认的分配器
list <string, __gnu_cxx::malloc_allocator<string>> c2; // 3110
list <string, __gnu_cxx::new_allocator<string>> c3; // 3156
list <string, __gnu_cxx::__pool_alloc<string>> c4; // 4922
list <string, __gnu_cxx::__mt_alloc<string>> c5; // 3297
list <string, __gnu_cxx::bitmap_allocator<string>> c6; // 4781
/** 交互,选择要使用的分配器(6种) */
int choice;
long value;
cout << "select: "
<< " (1) std::allocator "
<< " (2) malloc_allocator "
<< " (3) new_allocator "
<< " (4) __pool_alloc "
<< " (5) __mt_alloc "
<< " (6) bitmap_allocator ";
cin >> choice;
if (choice != 0) {
cout << "how many elements: ";
cin >> value;
}
/** 使用对应分配器分配内容并填充list */
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for (long i = 0; i < value; ++i) {
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", i);
switch (choice) {
case 1 :
c1.push_back(string(buf));
break;
case 2 :
c2.push_back(string(buf));
break;
case 3 :
c3.push_back(string(buf));
break;
case 4 :
c4.push_back(string(buf));
break;
case 5 :
c5.push_back(string(buf));
break;
case 6 :
c6.push_back(string(buf));
break;
default:
break;
}
}
catch (exception &p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "a lot of push_back(), milli-seconds : " << (clock() - timeStart) << endl;
/** 这里测试6种分配器 */
// test all allocators' allocate() & deallocate();
// (这种分配的用法不建议,因为要记住分配器分配了多少内存的空间,建议直接用容器)
int *p;
allocator<int> alloc1; // 定义分配器(int类型的默认分配器)
p = alloc1.allocate(1); // allocate 方法,分配1个元素(这里指一个int元素)
alloc1.deallocate(p, 1); // deallocate方法,交还指针和分配的空间(不建议这种用法)
__gnu_cxx::malloc_allocator<int> alloc2;
p = alloc2.allocate(1);
alloc2.deallocate(p, 1);
__gnu_cxx::new_allocator<int> alloc3;
p = alloc3.allocate(1);
alloc3.deallocate(p, 1);
__gnu_cxx::__pool_alloc<int> alloc4;
p = alloc4.allocate(2);
alloc4.deallocate(p, 2); //我刻意令參數為 2, 但這有何意義!! 一次要 2 個 ints?
__gnu_cxx::__mt_alloc<int> alloc5;
p = alloc5.allocate(1);
alloc5.deallocate(p, 1);
__gnu_cxx::bitmap_allocator<int> alloc6;
p = alloc6.allocate(3);
alloc6.deallocate(p, 3); //我刻意令參數為 3, 但這有何意義!! 一次要 3 個 ints?
}源码之分布(VC、GCC)
源码之前 了无秘密
标准库路径
- Visual C++
...\include...\include\cliext
- GUN C++
...\5.9.2\include\c++\bits(stl开头的头文件)...\5.9.2\include\c++\ext(扩充的)