效果实现
效果实现
目录
可拖拽div
前置知识——测量值
div测量
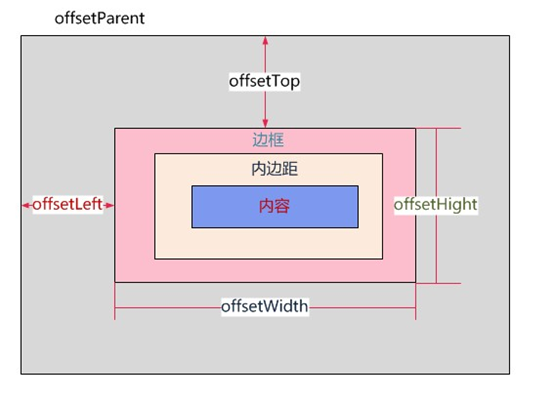
距离值——offsetLeft、offsetParent、offsetWidth
只读属性,返回当前元素左上角相对于
HTMLElement.offsetParent的左边界偏移的像素值返回值是一个整数
对块级元素来说,
offsetTop、offsetLeft、offsetWidth及offsetHeight描述了元素相对于offsetParent的边界框。
距离值——offsetLeft、style.left
表格中的box为document.getElementById("box")的结果
| 比较 | offsetLeft | left |
|---|---|---|
| 写法 | box.offsetLeft | box.style.left |
| 读写 | 只读 | 可读写 |
| 返回值 | 数字。如:55 | 带单位的字符串。如:'55px' 转化: parseInt(box.style.left.replace('px','')) |
| 值 | 对块级元素,是到offsetParent边框的距离offsetParent是最近的带定位的父元素,若无均指定则为body | |
| bug | 计算没有定位的盒子时会出问题 没有指定left样式时也可能返回空字符串 |
大小值——clientWidth、offsetWidth、scrollWidth
均以像素计,把Heitht替换成Width同理
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| clientWidth | content + padding*2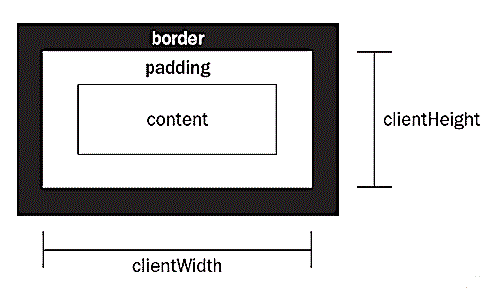 |
| offsetWidth | content + padding*2 + border*2 |
| scrollWidth | 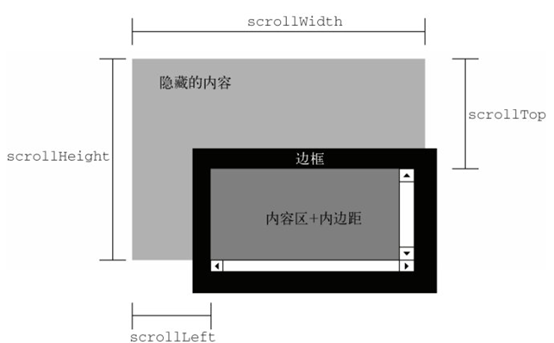 |
鼠标测量
距离值——offsetX、clientX、pageX、screenX、x
offsetX、offsetY // 相对于带有定位的父盒子的x,y坐标
clientX、clientY // 距离当前body可视区域的x,y坐标
pageX、pageY // 对于整个页面来说,包括了被卷去的body部分的长度
// 即:e.pageX == e.clientX + document.documentElement.scrollLeft
screenX、screenY // 点击位置距离当前电脑屏幕的x,y坐标
x、y // 同screenX、screenY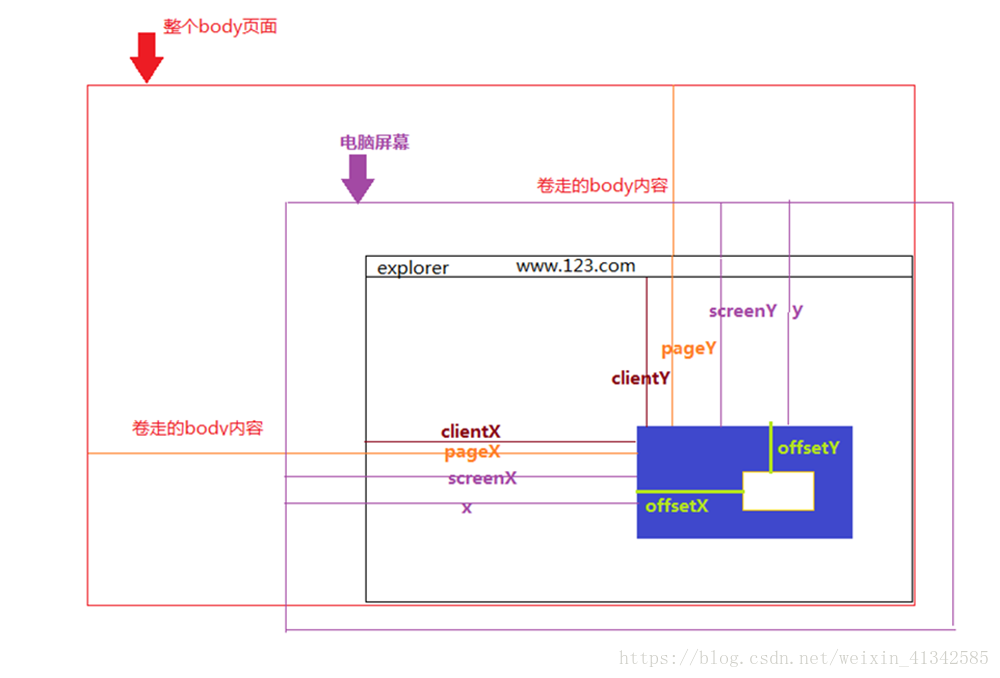
捕获——setCapture、releaseCapture
setCapture鼠标捕获
作用是将鼠标事件捕获到当前文档的指定的对象——对指定的对象设置鼠标捕获
这个对象会为当前应用程序或整个系统接收所有鼠标事件。
releaseCapture释放鼠标捕获
并触发onlosecapture事件
页面测量
大小测量——clientWidth、offsetWidth 、scrollWidth
clientWidth、offsetWidth 、scrollWidth区别同div测量
// 网页可见区域宽高
document.body.clientWidth // 2543,滚动条占17
document.body.clientHeight // 478,仅包含正文
// 网页可见区域宽高(包括边线的宽高)
document.body.offsetWidth // 2543,滚动条占17
document.body.offsetHeight // 478,仅包含正文
// 网页正文全文宽高
document.body.scrollWidth // 2543,滚动条占17
document.body.scrollHeight // 500,包含了被卷曲的地方距离测量——scrollLeft
// 网页被卷去的高左
document.body.scrollTop // 0,好像测不出来...
document.body.scrollLeft // 0,好像测不出来...屏幕测量
大小测量——screen.width、screen.availWidth
// 屏幕分辨率的高宽
window.screen.height // 1440
window.screen.width // 2560
// 屏幕可用工作区高宽
window.screen.availHeight // 1410,估计是减去了状态栏的30
window.screen.availWidth // 2560距离测量——screenLeft、screenX
// 网页正文部分上左
window.screenTop // -8,少了8?
window.screenLeft // -8or2552,少了8?能计算双屏
// 网页正文部分上左(与上结果一致)
window.screenX // -8,少了8?
window.screenY // -8or2552,少了8?能计算双屏总体测量——screen
window.screen // 返回一个对象,包含屏幕高宽和距离,这次距离没有少8大小拖拽
参考文章
效果(动图)
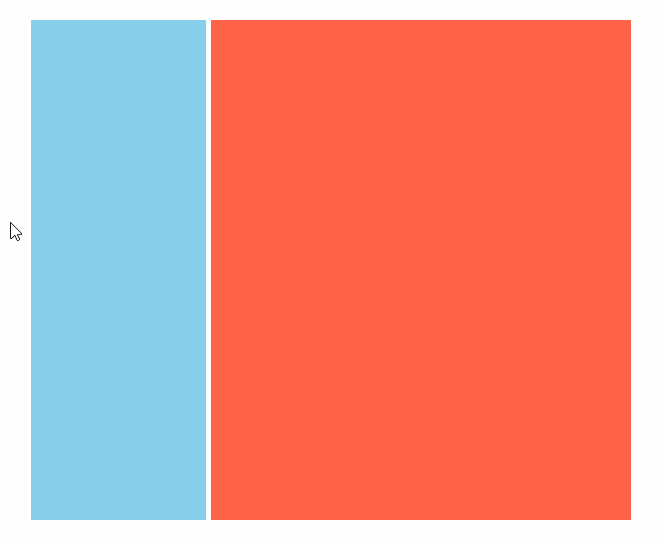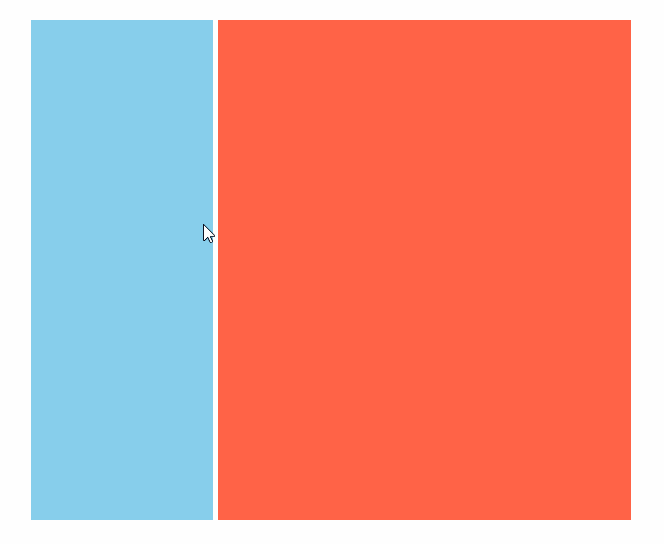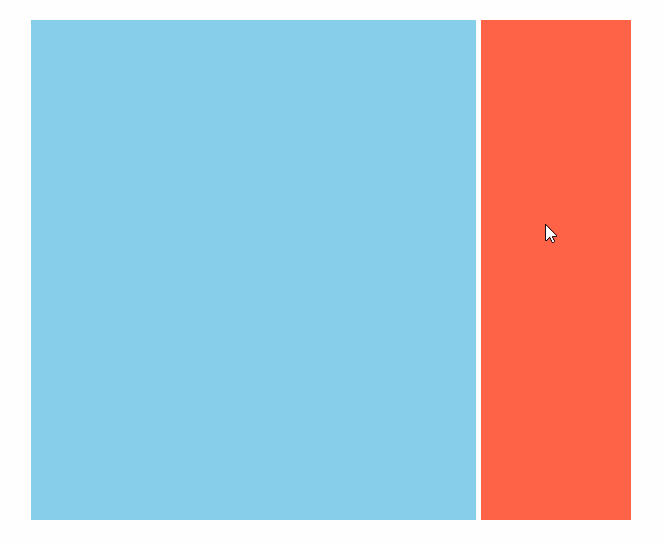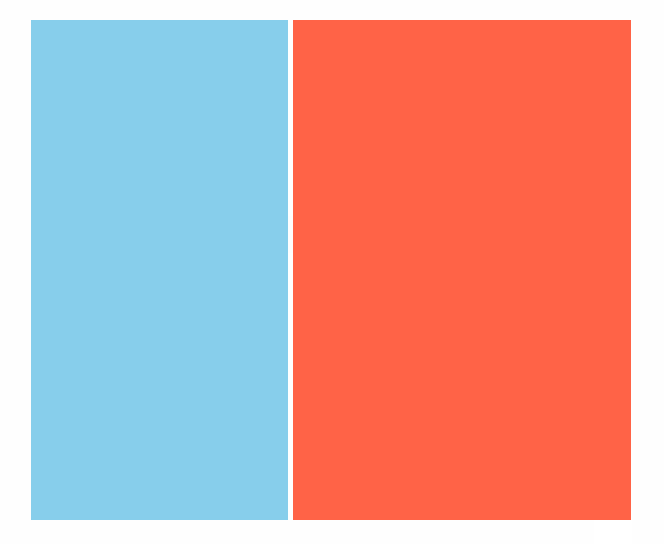
代码
代码
html
<div id="box">
<div id="left"></div>
<div id="resize"></div>
<div id="right"></div>
</div>css
body,html{
margin:0;
padding:0;
height:100%;
}
#box{ /*大容器*/
width:600px;
height:500px;
overflow:hidden;
}
#left{ /*左侧容器*/
width:calc(30% - 5px);
height:100%;
background:skyblue;
float:left;
}
#resize{ /*改变大小的边栏*/
width:5px;
height:100%;
cursor: w-resize; /*调整大小的图标*/
float:left;
}
#right{ /*右侧容器*/
float:right;
width:70%;
height:100%;
background:tomato;
}javascript
window.onload = function(){
var resize = document.getElementById("resize");
var left = document.getElementById("left");
var right = document.getElementById("right");
var box = document.getElementById("box");
resize.onmousedown = function(e){ // 鼠标按下事件
var startX = e.clientX; // 鼠标开始的X坐标
resize.left = resize.offsetLeft; // 边条左侧到父容器左侧的距离
document.onmousemove = function(e){ // 鼠标移动事件
var endX = e.clientX; // 鼠标现在的x坐标
var moveLen = resize.left + (endX - startX); // 移动后左侧的总长度 = 边条到左侧的距离 + (鼠标现在x坐标 - 鼠标开始x坐标)
var maxT = box.clientWidth - resize.offsetWidth; // 可移动的宽度距离 = 大容器宽度 - 边条长度
if(moveLen<150) moveLen = 150; // 判断是否小于指定的最小值,若是则不再移动
if(moveLen>maxT-150) moveLen = maxT-150; // 同理判断右侧
resize.style.left = moveLen; // 设置边框偏移
left.style.width = moveLen + "px"; // 设置左容器大小
right.style.width = (box.clientWidth - moveLen - 5) + "px"; // 设置右容器大小
}
document.onmouseup = function(evt){ // 鼠标松开时间
document.onmousemove = null; // 释放事件
document.onmouseup = null; // 释放事件
resize.releaseCapture && resize.releaseCapture(); // 释放鼠标捕获
}
resize.setCapture && resize.setCapture(); // 鼠标捕获
return false; // 这个应该是阻止默认行为...吧
}
}位置拖拽
插件介绍
鼠标位置追踪
demo(简易)
var box = document.getElementById("box");
document.mousedown = (e) => {
var e = e || window.event; //兼容浏览器 IE8以下(包含IE8)不支持e只支持window.event
var pageX = e.pageX || e.clientX + document.documentElement.scrollLeft; //获取鼠标距离页面左边距
var pageY = e.pageY || e.clientY + document.documentElement.scrollTop; //获取鼠标距离页面上边距
box.offsetLeft=(pageX/document.body.scrollWidth)/400 // box的x偏移
box.offsetTop=(pageY/document.body.scrollHeight)/200 // box的y偏移
}<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
<title>测试</title>
</head>
<body style="width: 800px;height: 800px;">
<div id="box" style="position:absolute;background-color: blue;width: 200px;height: 200px; left:480px">111222</div>
<div id="box2" style="position:absolute;background-color: red;width: 200px;height: 200px; left:500px">111222</div>
</body>
</html>
<script>
window.onload = function(){
let box = document.getElementById("box");
let boxleft = parseInt(box.style.left.replace('px',''))
let box2 = document.getElementById("box2");
let box2left = parseInt(box2.style.left.replace('px',''))
document.onmousemove = (e) => {
let pageX = e.pageX; //获取鼠标距离页面左边距
let pageY = e.pageY; //获取鼠标距离页面上边距
box.style.left=boxleft+(pageX)/8+'px'
box2.style.left=box2left+(pageX)/10+'px'
}
}
</script>链接到当前文件 0
没有文件链接到当前文件